Knee pain can slowly take away your freedom — the freedom to walk comfortably, climb stairs, go to work, exercise, play with grandchildren, or simply enjoy life. When knee pain becomes severe and does not improve even after medicines, injections, physiotherapy, or lifestyle changes, doctors may recommend a procedure called Total Knee Replacement (TKR), also known as Total Knee Arthroplasty.
Add Your Heading Text Here
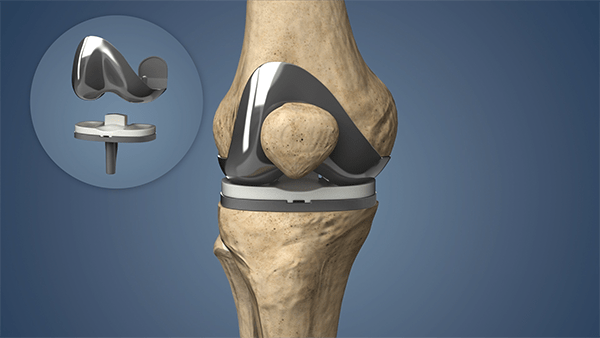
Before understanding the surgery, it is important to know how the knee works.
The knee is one of the largest and most important joints in the human body. It acts like a hinge joint, helping you:
- Walk
- Run
- Sit
- Stand
- Climb stairs
- Bend your legs
The knee joint is formed by three main bones:
- Femur — the thigh bone
- Tibia — the shin bone
- Patella — the kneecap
Between these bones, there is a smooth, cushion-like layer called cartilage. This cartilage allows bones to glide smoothly over each other without friction. There are also ligaments, tendons, and muscles around the knee that help in stability and movement.
So, when does the problem start?
Due to age, wear-and-tear, arthritis, injury, or medical conditions, the cartilage in the knee gets damaged. When cartilage wears away completely, the bones rub directly against each other. This causes:
- Severe pain
- Swelling
- Stiffness
- Reduced movement
- Difficulty walking or climbing stairs
- Cracking/grinding sounds
- Joint deformity in severe cases
When this condition becomes unbearable and medicines no longer help, knee replacement surgery becomes a powerful life-changing solution.
What is Total Knee Replacement?
Total Knee Replacement is a surgical procedure where the damaged knee joint surfaces are removed and replaced with artificial parts called prosthetic implants. These implants are made of strong and high-quality medical-grade metal and plastic.
In simple words:
👉 The damaged knee surface is removed
👉 A new artificial joint is fitted in its place
👉 The new joint works smoothly, reducing pain and improving movement
So instead of repairing the damaged cartilage, doctors replace the worn-out joint surfaces completely. That is why it is called “Total” Knee Replacement.
This surgery helps patients:
- Walk without pain
- Perform daily activities comfortably
- Improve mobility
Get back to a normal lifestyle
Types of Knee Replacement Surgery
Depending on the condition of your knee, doctors may recommend different types of knee replacement procedures.
1. Total Knee Replacement (Most Common)
Both sides of the knee joint (femur and tibia surface) are replaced with artificial implants. This is usually done when arthritis or damage affects the entire knee joint.
2. Partial Knee Replacement
Only one part (compartment) of the knee is damaged — usually the inner or outer portion. In such cases, only that section is replaced instead of the whole knee. This is also called unicompartmental knee replacement.
3. Bilateral Knee Replacement
When both knees are severely damaged, doctors may replace both knees in one surgery (simultaneous replacement) or one after the other in separate surgeries (staged replacement).
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is total knee replacement?
Total knee replacement is a surgery where damaged knee joint surfaces are replaced with artificial implants to relieve pain and improve movement.
2. Why is total knee replacement surgery done?
It is recommended for severe arthritis, chronic knee pain, stiffness, deformity, or when medicines, injections, and physiotherapy fail to provide relief.
3. Who is a good candidate for total knee replacement?
People with severe knee pain, difficulty walking, swelling, stiffness, knee deformity, and advanced osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis may need surgery.
4. Is total knee replacement a painful procedure?
With modern anesthesia and pain-management techniques, patients experience minimal pain, and discomfort gradually reduces within weeks.
5. How long does total knee replacement surgery take?
The procedure usually takes about 60 to 90 minutes, depending on the patient’s condition and surgical technique.
6. What are the risks of total knee replacement surgery?
Possible risks include infection, blood clots, implant loosening, stiffness, and anesthesia-related complications, although serious complications are rare.
7. How long does a knee replacement last?
Modern knee implants generally last 15–20 years or more, depending on activity level, lifestyle, and proper care.
8. How long is the recovery time?
Most patients walk within 1–2 days, resume routine activities in 4–6 weeks, and achieve full recovery in 3–6 months with physiotherapy.
9. Can both knees be replaced at the same time?
Yes, in selected patients this is possible depending on overall health, fitness level, and doctor’s recommendation.
10. What activities can I do after total knee replacement?
Patients can walk, climb stairs, drive, travel, and do daily activities comfortably. Low-impact exercises are encouraged while high-impact sports are usually avoided.
Table of Contents
Candidates
The Candidates section explains who may need total knee replacement and when it is recommended.
Consultation
The Consultation section describes what happens during a knee replacement consultation and evaluation.
Questions
The Questions section covers important doubts patients should clarify before surgery.
Risks and Safety
The Risks and Safety section explains possible complications and how the procedure is kept safe.
Cost
The cost of total knee replacement surgery varies based on implant type, hospital facilities, surgical approach, and postoperative care needs.
Preparation
Preparation includes medical evaluation, medication review, prehabilitation exercises, home planning, and understanding the recovery plan.
Steps
The procedure involves removing damaged joint surfaces, positioning artificial components, restoring alignment, and completing surgical closure with postoperative care. Steps
Recovery
Recovery includes pain management, early mobilization, structured physiotherapy, gradual strength gains, and scheduled follow-up visits.
Results
Most patients experience significant pain relief, improved knee stability, better mobility, and enhanced daily function. Results
Before-and-after
Before-and-after results commonly show reduced pain, improved alignment, increased walking ability, and better overall knee movement.
Choosing the right surgeon
Choosing the right surgeon involves assessing experience in joint replacement, patient outcomes, communication clarity, and access to comprehensive rehabilitation.